Whatever operation developers or administrators are performing on the Magento shop, it is not simple. And although though running into Magento 2 issues is something no one ever wants to do, they can happen while upgrading Magento, installing Magento 2 extensions, making numerous requests for products, running scripts or files without the proper execute rights, etc.
These Magento problems can be simple to rather complicated, impacting the functionality and user experience of your website. They are, however, typically manageable if you recognize their timing of appearance. Let’s explore the most common issues with Magento 2 and their fixes.
Most Common Magento 2 Problems and Solutions
1. Access Denied
The Magento admin area is where the Magento Access Denied HTTP error 403 most frequently arises. It happens when you attempt to visit a page that you are not authorized to see due to incorrect login information, an incorrect user role, or the installation of Magento 2 extensions.
How to fix Magento 2 ‘Access Denied’ Error
a) Get correct credentials
The only way to recover your admin panel login credentials is by using the database tables. Run the next SQL query in your database by going there:
SET @salt = MD5(UNIX_TIMESTAMP()); UPDATE admin_user SET password = CONCAT(SHA2(CONCAT(@salt, 'YourNewPassword'), 256), ':', @salt, ':1') WHERE username = 'admin';
Now attempt to log in using the new password. If you are unable to do so, check the first failure and lock expires columns in the admin user table and set their values to null.
b) Assign proper user role
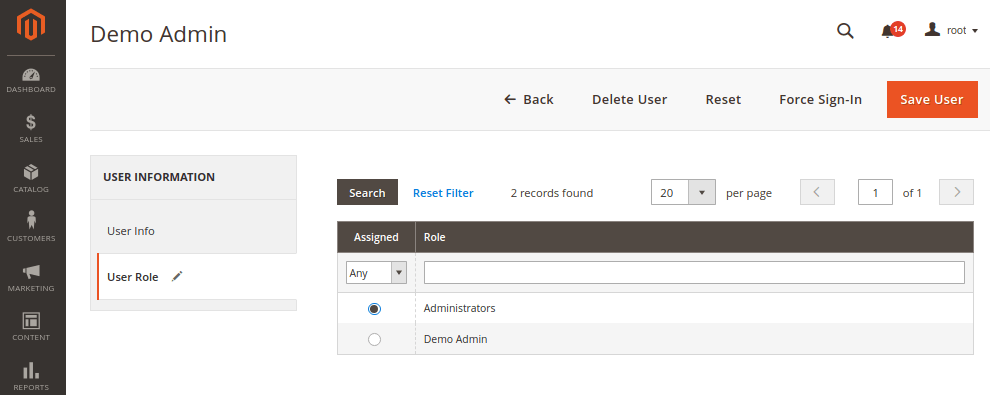
After adding a new user to Magento, if you get the "Access forbidden" problem, it’s likely because you haven’t given them a user role.
In this situation, either log in using a different account or request that the administrator go to System > Permissions > All Users and add your user to a specific user role.
c) Get permissions to access a particular extension
You might not have access to see new extension settings because Magento doesn’t automatically update rights to new extensions. Re-logging into the admin interface frequently helps. Reset admin permissions if the Magento “Access denied” problem still appears.
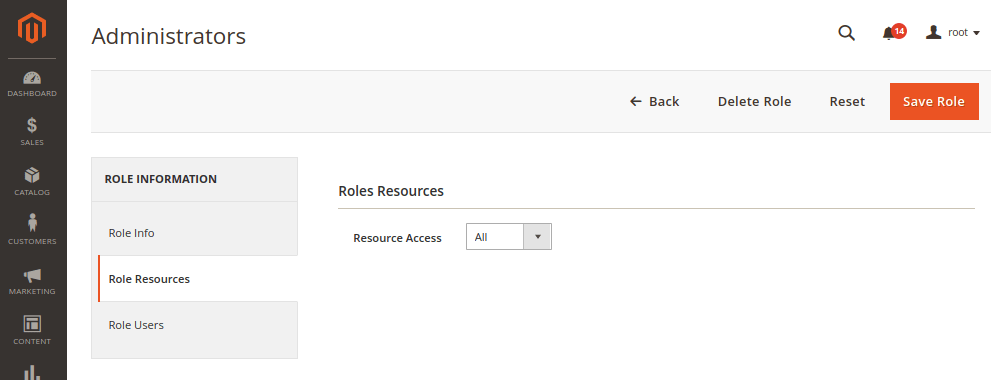
- Locate the role for which the new extension is restricted by going to
System > Permissions > User Roles. - In the
Role Resourcessection, changeResource Accessto All or a specific extension.
d) Fix the system.xml and config.xml conflict
The “Access forbidden” bug in Magento 2 might occasionally emerge after activating some custom modules and prohibit you from accessing the custom module.
Try turning off the extension to see if the problem persists. If so, look at the config.xml and system.xml files. There may be blank spaces in the config.xml and system.xml files.
2. Internal Server Error 500
The standard 500 HTTP status code error that shows when the server is unable to provide the requested page is the Magento internal server error. Reloading the page could work, but more often than not, you’ll need to look through the server logs to learn more about the problem.
How to fix Magento 2 Internal Server Error 500
Enable developer mode and remove the comment from the following line before continuing. You can quickly debug Magento and receive the specific errors in the error log, in the app/bootstrap.php file.
#ini_set('display_errors', 1);
a) Change File Permissions
When you attempt to access the Magento admin panel or the connect manager when the Magento permission files are incorrectly set, the Magento internal server error most frequently manifests.
After Magento installation, the index files’ default permission is 664 while it should be 644. Run the following instructions in the index.php file located in the Magento root to modify the default file permissions from 664 to 644.
find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find ./var -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \;
find ./pub/media -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \;
find ./pub/static -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \;
chmod 777 ./app/etc
chmod 644 ./app/etc/*.xml
chmod u+x bin/magento
b) Increase Memory Limit
For the Magento platform to operate properly, specific system capabilities are needed. This does apply to some PHP memory restrictions. The default memory limit supplied by Magento hosting providers is often 20MB or 60MB, which is insufficient for Magento.
The php memory limit setting in the php.ini or .htaccess files has to be increased to 756M in order to resolve the Magento internal server error 500.
- Use SSH to connect to your website server.
- Locate the php.ini file’s folder and use the vi editor to access it.
- Add the next line to it.
memory_limit = 756M
- If the value is too low, raise it.
c) Rename .htaccess File
Setting up the .htaccess file correctly is crucial since any mistakes or typos might result in problems, such as the Magento 2 500 internal server error. When you install plugins, patches, or themes, problems in the .hraccess file arise and call for appropriate adjustments.
d) Disable Third-party Extensions
To determine whether the problem will be resolved, try deleting or renaming the .htaccess file.
After you install or upgrade any third-party Magento extensions, Internal Server Error may happen. The new extension or version and the already installed modules on your shop are typically at odds with one another.
To remove the extension, use the next command:
php bin/magento mod:disable VenorName_ModuleName
Once you’ve ran it, reach the seller to know more and request the remedy.
e) Disable Maintenance Mode
When maintenance mode is enabled, the root folder of Magento receives the maintenance.flag file. As a result, web browsers cannot run the modified index.php file, which now has permission 666.
To remove the upkeep, enter the following command.
Set the permission for the file to 755 and flag it.
php bin/magento maintenance:disable
3. 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable
The other frequent problem with Magento 2 is Error 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable, which can occur when you attempt to access Magento admin or storefront after installing Magento extensions or Magento. Typically, this paragraph follows it:
“The server is temporarily unable to service your request due to maintenance downtime or capacity problems. Please try again later” or “The server is temporarily unable to handle the request”. It indicates that the server cannot immediately handle your request or that it may be improperly configured.
How to fix Magento 2 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable error
Now that you are aware of the cause of the Service Temporary Unavailable problem, you can easily resolve it.
Fixing the Magento 2 issue 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable
1. Delete the .maintenance.flag file located in the var folder in the Magento 2 root directory.
2. Clear the Magento cache using the admin panel or this command:
php bin/magento cache:flush
You can also notice the following notifications after deleting the problematic file:
Exception printing is disabled by default for security reasons — to fix it, turn on developer mode to view the problematic code. To activate developers mode, use the following command:
php bin/magento deploy:mode:set developer
Update your database to resolve the error, go to the Magento root directory and execute:
php bin/magento setup:upgrade
4. bash: bin/magento: Permission denied
When attempting to execute a script or file that does not have execute rights, you often receive the bash permission refused error. One of the most frequent Magento issues is this one. Simply changing the file permissions and adding executive one will cure the issue.
How to fix Bash Permission Denied error
To fix the bash permission denied error follow these steps:
1. Open terminal (shell)
2. Navigate to the folder with the script
3. Run the CLI command to change file permission settings:
chmod +x path_to_file/file_name
For example, if you run a Magento 2 CLI command:
bin/magento ...
and get the error:
bash: bin/magento: Permission denied
You need to add an execute (x) permission to the bin/magento file.
For this, please run the CLI command:
chmod +x bin/magento
In case of Magento 2 you can also use the next command to avoid the issue (php before bin/magento):
php bin/magento ...
5. No such entity
The “No such entity.”, “No such entity with” or “No such entity with customerId” error messages in Magento 2 typically appear when you attempt to load an unexisting object using the Magento 2 Repository Class.
How to fix Magento 2 No such entity error
Please open the following file to begin troubleshooting this typical Magento 2 error:
vendor/magento/framework/Exception/NoSuchEntityException.php
Then add a temporary debug backtrace code at the start of the __construct method:
foreach (debug_backtrace() as $_stack) {
echo ($_stack["file"] ? $_stack["file"] : '') . ':' .
($_stack["line"] ? $_stack["line"] : '') . ' - ' .
($_stack["function"] ? $_stack["function"] : '');
}
exit();
Refresh the page after saving the file.
You will view the debug backtrace, which will enable you to identify the root cause of the problem and get insight on how to solve it.
This issue is typically caused by third-party Magento 2 extensions, therefore you may modify their code and add a “try-catch” exception.
Remember to undo your modifications in the NoSuchEntityException.php file after you’re done.
Magento is a sophisticated system with many built-in capabilities that you can modify or enhance using various third-party tools. As a result, operating Magento necessitates routine troubleshooting to identify and resolve any problems.
Knowing the causes of the most frequent Magento issues will enable you to quickly resolve them and guarantee that your business runs more efficiently.

